正常 C57BL/6J 小鼠的被毛为黑色,耳朵、眼睛和尾巴周围的毛发可呈现较浅的颜色(黄色/浅棕黄色);然而,老龄鼠可能会表现出以下这些自然衰老的特征:
- 灰白色被毛
- 毛发稀疏

老龄B6小鼠表现出灰白色背毛和毛发稀疏。
除了由于衰老而产生的正常特征(被毛变灰白或变稀疏)外,在我们 25 周龄之后的鼠群中还会出现某些特征,包括:
- 理毛:因小鼠的群居社交活动而引起的一种脱毛现象。因此,我们发送的老龄鼠可能会有脱毛或毛发/胡须稀疏的情况,这与衰老无关;但是我们的鼠群中不会出现炎症或皮炎等健康问题。

老龄B6小鼠出现理毛现象。
- 请勿将不同运输箱中的小鼠放到同一鼠笼中饲养。小鼠从离乳后立即进行分笼饲养,离乳时分在同一饲养笼中的小鼠可以生活在一起,如果之后将它们和不同鼠笼的小鼠饲养在一起,会出现相互攻击和打斗的现象。
- 将鼠笼放置在远离通道等易出现人流、噪音和振动的位置,并让笼子与墙壁之间保持一定的距离,以便尽可能将饲养环境中的噪音、振动和其他干扰降到最低。
- 护理和抓取小鼠时要轻柔、缓慢、安静,并尽可能减少护理和抓取次数。
- 增加筑巢料及富集物,如纸制隧道和玩具小屋,可以减少小鼠理毛行为。

老龄 B6 小鼠可出现口鼻部脱毛现象。
- 不支持按动物的重量下单,不可指定无掉须或脱毛的小鼠。
- 暂不支持特殊运输配置要求;小鼠将以在杰克森实验室设施中饲养时的分笼情况进行打包,每个饲养箱中小鼠数量最多为 10 只。
•临床生化
•身体成分分析
•器官重量
•脾脏的流式细胞仪分析显示,初始 T 细胞呈年龄依赖性降低,调节性 T 细胞和效应/效应记忆 T 细胞增加
Arriola Apelo SI, Pumper CP, Baar EL, Cummings NE, Lamming DW. Intermittent Administration of Rapamycin Extends the Life Span of Female C57BL/6J Mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016 Jul;71(7):876-81. PMID: 27091134
Dodds SG, Livi CB, Parihar M et al. Adaptations to chronic rapamycin in mice. Pathobiol Aging Age Relat Dis. 2016 May 27;6:31688. doi: 10.3402/pba.v6.31688. PMID:27237224
Gardner LE, White JD, Eimerbrink MJ, Boehm GW, Chumley MJ. Imatinib methanesulfonate reduces hyperphosphorylation of tau following repeated peripheral exposure to lipopolysaccharide. Neuroscience. 2016 Sep 7;331:72-7. PMID: 27320209
Joanisse S, Nederveen JP, Baker JM, Snijders T, Iacono C, Parise G. Exercise conditioning in old mice improves skeletal muscle regeneration. FASEB J. 2016 Jun 15. pii: fj.201600143RR. PMID: 27306336
Kan NW, Ho CS, Chiu YS, Huang WC, Chen PY, Tung YT, Huang CC. Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation and Exercise Training on Exercise Performance in Middle-Aged Mice. Molecules. 2016 May 18;21(5). pii: E661. doi: 10.3390/molecules21050661.PMID: 27213310
Krishnan VS, White Z, McMahon CD, Hodgetts SI, Fitzgerald M, Shavlakadze T, Harvey AR, Grounds MD. A Neurogenic Perspective of Sarcopenia: Time Course Study of Sciatic Nerves From Aging Mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2016 May;75(5):464-78. PMID: 27030741
Lee BP, Pilling LC, Emond F, Flurkey K, Harrison DE, Yuan R, Peters LL, Kuchel GA, Ferrucci L, Melzer D, Harries LW. Changes in the expression of splicing factor transcripts and variations in alternative splicing are associated with lifespan in mice and humans. Aging Cell. 2016 Jun 30. doi: 10.1111/acel.12499. PMID: 27363602
Mock BE, Vijayakumar S, Pierce J, Jones TA, Jones SM. Differential effects of Cdh23(753A) on auditory and vestibular functional aging in C57BL/6J mice. PMID: 27255811
Oh YS, Seo EH, Lee YS ET AL. increase of Calcium Sensing Receptor Expression Is Related to Compensatory Insulin Secretion during Aging in Mice. PLoS One. 2016 Jul 21;11(7):e0159689. PMID: 27441644
Perry RA Jr, Brown LA, Lee DE, Brown JL, Baum JI, Greene NP, Washington TA. Differential effects of leucine supplementation in young and aged mice at the onset of skeletal muscle regeneration. Mech Ageing Dev. 2016 Jun 18;157:7-16. PMID: 27327351
Wang L, Du Y, Wang K, Xu G, Luo S, He G. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces memory deficits and facilitates Aβ generation in C57BL/6J mice. Exp Neurol. 2016 Jul 12;283(Pt A):353-364. PMID: 27421879
White Z, White RB, McMahon C, Grounds MD, Shavlakadze T. High mTORC1 signaling is maintained, while protein degradation pathways are perturbed in old murine skeletal muscles in the fasted state. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Jun 22;78:10-21. PMID: 27343428
Allard JS, Perez EJ, Fukui K, Carpenter P, Ingram DK, de Cabo R. Prolonged metformin treatment leads to reduced transcription of Nrf2 and neurotrophic factors without cognitive impairment in older C57BL/6J mice. Behav Brain Res. 2016 Mar 15;301:1-9. PMID: 26698400
Hayama T, Murakami K, Watanabe T, Maeda R, Kamata M, Kondo S. Single administration of a novel γ-secretase modulator ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in aged C57BL/6J mice. Brain Res. 2016 Feb 15;1633:52-61. PMID: 26707406
M. L. Porto et al. Reactive oxygen species contribute to dysfunction of bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells in aged C57BL/6 J mice. Journal of Biomedical Science 2015, 22:97. PMID: 26498041
Romanova EV, Rubakhin SS, Ossyra JR, Zombeck JA, Nosek MR, Sweedler JV, Rhodes JS. Differential peptidomics assessment of strain and age differences in mice in response to acute cocaine administration. J Neurochem. 2015 Dec;135(5):1038-48. PMID: 26223348
Allard JS, Perez EJ, Fukui K, Carpenter P, Ingram DK, de Cabo R. Prolonged metformin treatment leads to reduced transcription of Nrf2 and neurotrophic factors without cognitive impairment in older C57BL/6J mice. Behav Brain Res. 2016 Mar 15;301:1-9. PMID: 26698400
Hayama T, Murakami K, Watanabe T, Maeda R, Kamata M, Kondo S. Single administration of a novel γ-secretase modulator ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in aged C57BL/6J mice. Brain Res. 2016 Feb 15;1633:52-61. PMID: 26707406
M. L. Porto et al. Reactive oxygen species contribute to dysfunction of bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells in aged C57BL/6 J mice. Journal of Biomedical Science 2015, 22:97. PMID: 26498041
Romanova EV, Rubakhin SS, Ossyra JR, Zombeck JA, Nosek MR, Sweedler JV, Rhodes JS. Differential peptidomics assessment of strain and age differences in mice in response to acute cocaine administration. J Neurochem. 2015 Dec;135(5):1038-48. PMID: 26223348
Kane AE, Hilmer SN, Boyer D, Gavin K, Nines D, Howlett SE, de Cabo R, Mitchell SJ. Impact of Longevity Interventions on a Validated Mouse Clinical Frailty Index. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016 Mar;71(3):333-9. PMID: 25711530
Saroja SR, Kim EJ, Shanmugasundaram B, Höger H, Lubec G. Hippocampal monoamine receptor complex levels linked to spatial memory decline in the aging C57BL/6J. Behav Brain Res. 2014 May 1;264:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.01.042. PMID: 24508236
Shanks RA, Ross JM, Doyle HH, Helton AK, Picou BN, Schulz J, Tavares C, Bryant S, Dawson BL, Lloyd SA. Adolescent exposure to cocaine, amphetamine, and methylphenidate cross-sensitizes adults to methamphetamine with drug- and sex-specific effects. Behav Brain Res. 2015 Mar 15;281:116-24. PMID: 25496784
Zhang Y, Brownstein AJ, Buonora M, Niikura K, Ho A, Correa da Rosa J, Kreek MJ, Ott J. Self administration of oxycodone alters synaptic plasticity gene expression in the hippocampus differentially in male adolescent and adult mice. Neuroscience. 2015 Jan 29;285:34-46. PMID: 25446355
Neff F, Flores-Dominguez D et al. Rapamycin extends murine lifespan but has limited effects on aging. J Clin Invest. 2013. 123(8):3272-91. PMID:23863708
Ackert-Bicknell CL. HDL cholesterol and bone mineral density: Is there a genetic link? Bone. 2012 Feb;50(2):525-33. PMID: 21810493
Steegenga WT, de Wit NJ, Boekschoten MV,et al. Structural, functional and molecular analysis of the effects of aging in the small intestine and colon of C57BL/6J mice. BMC Med Genomics. 2012 Aug 28;5:38. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-5-38. PMID: 22929163
Wilkinson JE, Burmeister L, Brooks SV, Chan CC, Friedline S, Harrison DE, Hejtmancik JF, Nadon N, Strong R, Wood LK, Woodward MA, Miller RA. Rapamycin slows aging in mice. Aging Cell. 2012 Aug;11(4):675-82. PMID: 22587563
Capel F, Delmotte MH, Brun M, Lonchampt M, De Fanti B, Xuereb L, Baschet L, Rolland G, Galizzi JP, Lockhart B, Ktorza A, Dacquet C. Aging and obesity induce distinct gene expression adaptation in the liver of C57BL/6J mice. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. 2011;4(3):154-64. PMID: 21757924
Li Q, Zhao H, Zhao M, Zhang Z, Li Y. Chronic green tea catechins administration prevents oxidative stress-related brain aging in C57BL/6J mice. Brain Res. 2010 Sep 24;1353:28-35. PMID: 20682303
Elbaz A, Rivas D, Duque G. Effect of estrogens on bone marrow adipogenesis and Sirt1 in aging C57BL/6J mice. Biogerontology. 2009 Dec;10(6):747-55. PMID: 19333775
KI Andreasson, A Savonenko, S Vidensky Age-dependent cognitive deficits and neuronal apoptosis in cyclooxygenase-2 transgenic mice. The Journal of Neuroscience 2001 21(20): 8198-8209. PMID: 11588192
JAX 衰老研究中心利用生物学和基因组学方面的不同专业知识,研究与衰老相关的问题和疾病,有助于更好地理解寿命和健康寿命研究中的分子机制。查看来自 JAX 的老龄 B6 小鼠和其他小鼠模型的相关文献。
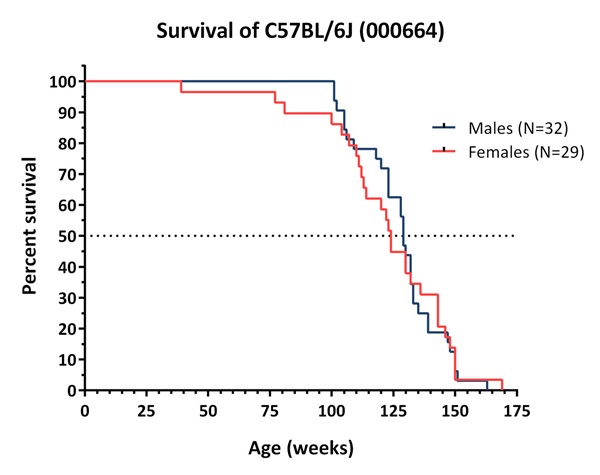
小鼠表型组数据库 (MPD) 是公开发布 Nathan Shock 中心生成的核心数据的主要数据库,并面向公众开放。MPD 公布了雄鼠和雌鼠的中位寿命和 Kaplan-Meier 生存曲线,以及所有品系的表型和基因型数据。
法务咨询
电话: 001-207-288-6470(美国)
电子邮件: TechTran@jax.org

 >
>